金沙集团3354.c.cav的产品展示navigation

电话:021-35183767
021-35183767
传真:021-35183767-8008
qq:2881513768
地址:上海市闵行区兴梅路485号 xingmei rd 485shanghaichina
ugo basile机械压痛仪
时间:2023-12-22来源:本站作者:玉研仪器
详细介绍
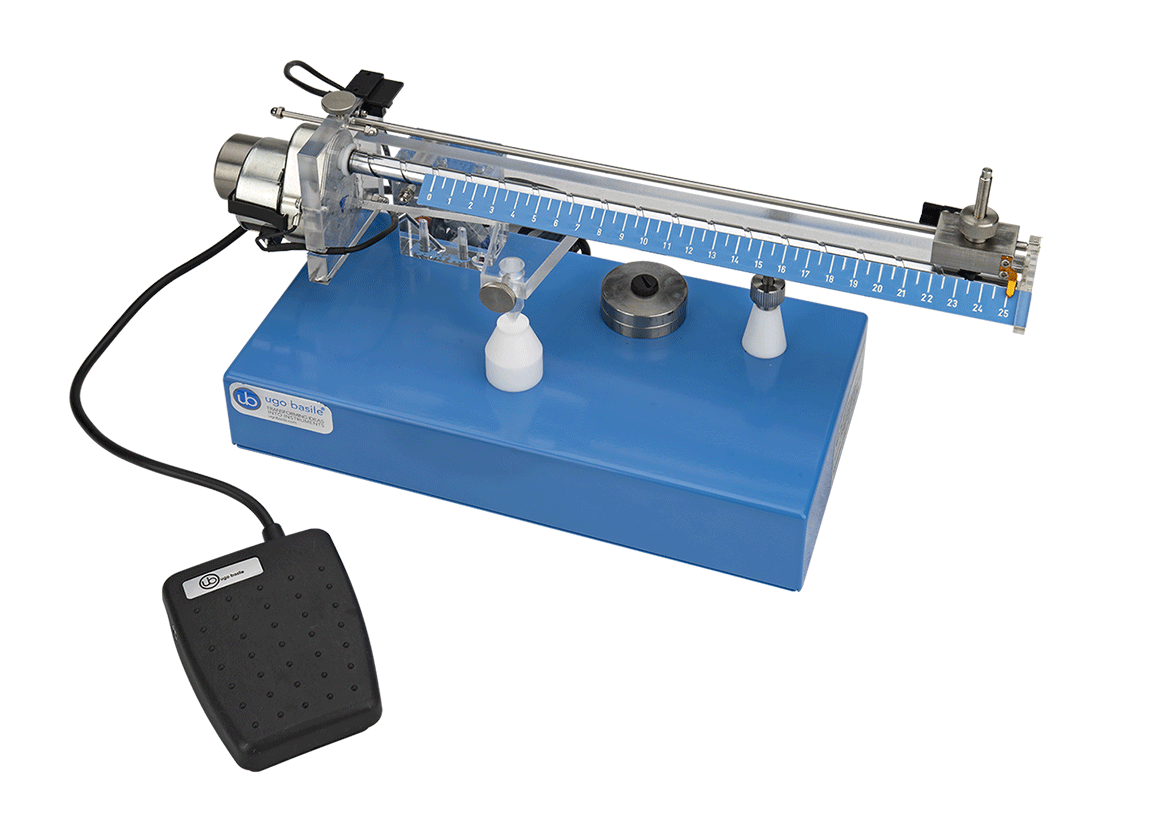
ugo basile机械压痛仪采用randall-selitto测痛法,通过自动化进行大小鼠鼠爪压痛阈值测试。已被证明在多学术和工业实验室研究中,有效帮助镇痛药物的快速精确筛选。
实验动物伤害感受性阈值的确定对于药物的抗伤害活性具有重要意义,常通过大小鼠后肢反应(缩跳跃、舔足、跳跃)确定,最常用的疼痛过敏方法为压痛测试。
ugo basile 机械压痛仪是一种量化对大小鼠后足背部施加线性增加的机械力,引发缩足反应的测试设备。是基于 randall 和selitto 于 1957 年研究成果(randall-selitto 测试法)开发而来,为评估镇痛药物影响疼痛组织对机械压力刺激反应阈值变化的经典工具。机械压痛仪避免了手动施加压力,提供了更好的刺激一致性,比传统的纤维丝和电子测痛仪更适合检测鼠爪整体机械痛阈值变化。
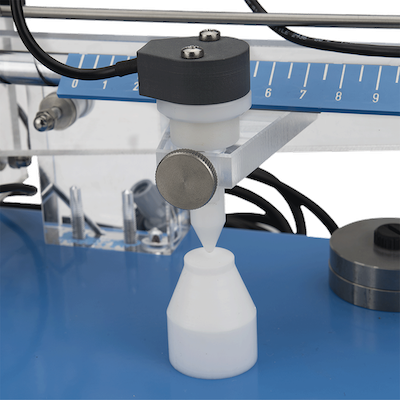
测试时,将大小鼠爪子置于底座和锥形刺激杆之间,驱动马达以恒定速率推动读数标尺上的重力砝码前进以增加锥形刺激杆的压力。当大小鼠出现缩足反应时,测试结果在读出标尺上读出。测试模块为具有生物惰性的材质组成,摩擦系数低,动物可轻松缩回爪子。
优势特点:
一、历史悠久,大量研究支持
ugo basile 机械压痛仪基于50多年的专业知识和持续的产品开发,测量机械刺激引起的大小鼠鼠爪伤害
感受阈值测量。自1965年以来,已有多个学术研究室使用ugo basile 机械压痛仪发表千篇文章。
二、经典的药物筛选设备
机械压痛仪具有脚爪整体机械痛刺激特点,而中枢神经对此最为为敏感,这对快速、精确筛选镇痛药物具有独特优势。
三、单机三种量程,施力恒定
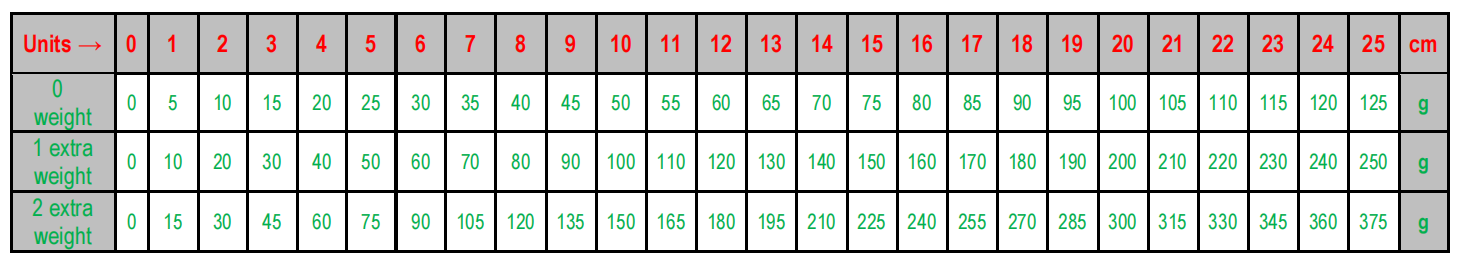
可设置0-250g、0-500g、0-750g三种量程,可满足大小鼠测试需求,电机自动化控制,性能稳定,排除了人为施力不恒定对测试结果的干扰。
四、无需校准,可升级数字式记录型号
设备无需校准,实验人员可控制脚踏开关实时结束测试。可升级成数字式记录型号检测鼠爪缩足现象并自动记录数据。
应用领域:
机械压痛仪可用于对正常和发炎的大小鼠爪进行快速精确的止痛药物筛选,以及对脊髓反射的有害刺激的反应阈值的测定,可检测脊髓损伤后神经病理性疼痛。其测试结果可的可复现性非常高,可轻松在不同实验室进行结果的复现。
| 37215 | 大小鼠通用机械压痛仪完整系统,包括电驱动主机、脚踏开关、压力砝码等 |
| 37216 | 小鼠专用型机械压痛仪完整系统,包括电驱动主机、脚踏开关、压力砝码等 |
| 37215-bundle | 数字式大小鼠通用机械压痛仪完整系统 |
| 37216-bundle | 数字式小鼠专用型机械压痛仪完整系统 |
| 37215-100 | 升级数字式组件 |

参考文献:
1.baloh, robert h et al. “transplantation of human neural progenitor cells secreting gdnf into the spinal cord of patients with als: a phase 1/2a trial.” nature medicine vol. 28,9 (2022): 1813-1822. doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01956-3
2.bosse, gabriel d et al. “the 5α-reductase inhibitor finasteride reduces opioid self-administration in animal models of opioid use disorder.” the journal of clinical investigation vol. 131,10 (2021): e143990. doi:10.1172/jci143990
3.bang, sangsu et al. “gpr37 regulates macrophage phagocytosis and resolution of inflammatory pain.” the journal of clinical investigation vol. 128,8 (2018): 3568-3582. doi:10.1172/jci99888
4.goebel, andreas et al. “passive transfer of fibromyalgia symptoms from patients to mice.” the journal of clinical investigation vol. 131,13 (2021): e144201. doi:10.1172/jci144201
5.sikandar, shafaq et al. “brain-derived neurotrophic factor derived from sensory neurons plays a critical role in chronic pain.” brain : a journal of neurology vol. 141,4 (2018): 1028-1039. doi:10.1093/brain/awy009
6.vidal-torres, alba et al. “bispecific sigma-1 receptor antagonism and mu-opioid receptor partial agonism: wlb-73502, an analgesic with improved efficacy and safety profile compared to strong opioids.” acta pharmaceutica sinica. b vol. 13,1 (2023): 82-99. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2022.09.018
7.mousa, shaaban a et al. “superior control of inflammatory pain by corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 via opioid peptides in distinct pain-relevant brain areas.” journal of neuroinflammation vol. 19,1 148. 15 jun. 2022, doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02498-8
8.zhou, danli et al. “inhibition of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase by paeoniflorin attenuates neuroinflammation and ameliorates neuropathic pain.” journal of neuroinflammation vol. 16,1 83. 11 apr. 2019, doi:10.1186/s12974-019-1476-6
9.wang, wenying et al. “exchange factor directly activated by camp-pkcε signalling mediates chronic morphine-induced expression of purine p2x3 receptor in rat dorsal root ganglia.” british journal of pharmacology vol. 175,10 (2018): 1760-1769. doi:10.1111/bph.14191
10.sala, emanuele et al. “improved efficacy, tolerance, safety, and abuse liability profile of the combination of cr4056 and morphine over morphine alone in rodent models.” british journal of pharmacology vol. 177,14 (2020): 3291-3308. doi:10.1111/bph.15049
您想了解更多详细资料吗?
请与我们联系:
tel:021-35183767,021-54377179
18502129044
qq:3007536621
微信:yuyanbio
mail:yuyanbio@126.com
欢迎您的咨询
